Rich and voiceless: How Putin has kept Russia's billionaires on side in the war
The term "oligarch" has become synonymous with Russia's wealthy business magnates who amassed significant wealth during the 1990s post-Soviet privatization period. These individuals capitalized on the rapid transfer of state assets into private hands, resulting in a power shift that saw a few becoming incredibly wealthy. This era laid the groundwork for the current socio-economic landscape in Russia, where wealth and political influence often intersect.
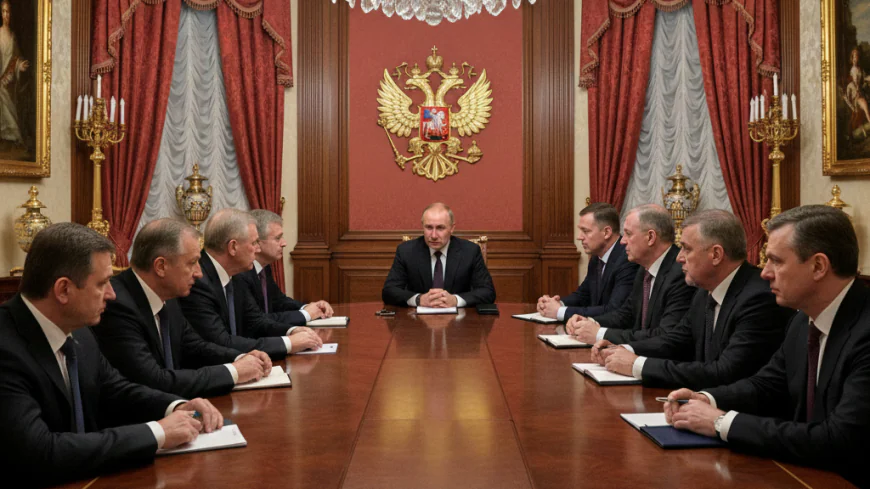

Rich and Voiceless: How Putin Has Kept Russia's Billionaires on Side in the War
TABLE OF CONTENTS
-
The Rise of Russian Oligarchs
-
Putin's Influence Over Billionaires
-
Economic Consequences and Sanctions
-
The Role of Loyalty and Patronage
-
International Perspectives
The Rise of Russian Oligarchs
During the reign of President Boris Yeltsin, the oligarchs gained substantial influence over the Russian economy and politics. However, the dynamic began to shift with the ascent of Vladimir Putin in 1999. Putin's approach was markedly different from that of his predecessor; he sought to consolidate power and establish a more centralized authoritative regime. This led to a realignment of power, where the oligarchs had to navigate an increasingly complex relationship with the Kremlin.
Putin's Influence Over Billionaires
Vladimir Putin's strategy has been to maintain a balance of power that ensures loyalty from the country's wealthiest individuals. This has been achieved through a combination of incentives and subtle coercion. Oligarchs were granted significant economic privileges, provided they aligned with the Kremlin's policies and refrained from political activities that could undermine Putin's authority.
The relationship between Putin and the oligarchs is underpinned by a mutual understanding: economic prosperity for loyalty and support. This arrangement has allowed the Russian president to maintain control over the country's major industries while ensuring that the oligarchs remain politically quiescent. The risks of dissent are clear, as demonstrated by the fate of those who have challenged the Kremlin, such as Mikhail Khodorkovsky, who was imprisoned after opposing Putin's policies.
Economic Consequences and Sanctions
The ongoing geopolitical tensions, particularly following Russia's annexation of Crimea in 2014 and the subsequent conflict in Ukraine, have led to a cascade of international sanctions targeting Russian businesses and individuals. These sanctions have aimed to exert pressure on the Kremlin by targeting the financial interests of Russia's elite.
Despite these sanctions, Putin has managed to retain the allegiance of key oligarchs. This can be attributed to his ability to shield them from the full impact of international isolation and offer alternative avenues for economic opportunities within Russia and allied nations. Moreover, the Kremlin's control over media and information flow has allowed it to present these sanctions as a Western attempt to weaken Russia, thereby fostering a sense of nationalism and unity among the oligarchs.
The Role of Loyalty and Patronage
Loyalty to the Kremlin is a cornerstone of the relationship between Putin and Russia's billionaires. This loyalty is not merely expected but is actively cultivated through a system of patronage, where the state provides economic opportunities and protection in exchange for unwavering support.
Oligarchs who adhere to this unwritten contract benefit from lucrative state contracts, access to natural resources, and positions within influential state-owned enterprises. This system of patronage reinforces the oligarchs' reliance on the Kremlin and discourages dissent. In return, they offer their resources and influence to support the government's domestic and international agendas.
International Perspectives
The international community views the relationship between Putin and Russian oligarchs with a mix of concern and strategic interest. Western nations, in particular, see the oligarchs as potential levers for applying pressure on the Kremlin. However, the effectiveness of this approach is often debated, given the complexities of Russia's political and economic systems.
While some Western policymakers advocate for increased sanctions and diplomatic pressure, others suggest engagement and dialogue as a means to influence Russia's domestic policies. The challenge lies in balancing these strategies to achieve desired outcomes without exacerbating tensions.
Ultimately, the relationship between Putin and Russia's billionaires is a testament to the intricate web of power, wealth, and politics that defines modern Russia. As the geopolitical landscape continues to evolve, the dynamics between these key players will remain a critical factor in shaping the country's future.
FAQ
Q: How did the Russian oligarchs initially gain their wealth?
A: Russian oligarchs gained their wealth during the 1990s through the privatization of state assets following the collapse of the Soviet Union. This period allowed a few individuals to acquire significant state resources at relatively low prices.
Q: What role do Russian oligarchs play in the country's economy?
A: Russian oligarchs control major sectors of the economy, including energy, banking, and natural resources. They wield significant economic influence, which is often aligned with the Kremlin's policies.
Q: How have international sanctions affected Russian oligarchs?
A: International sanctions have targeted the financial interests of Russian oligarchs, aiming to pressure the Kremlin. However, Putin has managed to mitigate some of these effects by offering alternative economic opportunities.
Q: Why do Russian oligarchs maintain loyalty to Vladimir Putin?
A: Loyalty is maintained through a system of patronage where the Kremlin offers economic privileges in exchange for political support and non-interference in state affairs.
Q: What is the international community's stance on the relationship between Putin and the oligarchs?
A: The international community is divided, with some advocating for increased sanctions to exert pressure, while others promote engagement and dialogue to influence Russia's policies.
Technical Evolution and Creative Innovation
The innovation showcased in this recent development highlights the transformative potential of modern digital tools in reshaping audience engagement. Industry leaders argue that the integration of advanced predictive analytics and human-centric design is no longer a luxury but a necessity for staying relevant in a competitive market. This shift also raises important ethical questions regarding data privacy and the role of automated decision-making in creative processes. As technology continues to bridge the gap between imagination and reality, the standards for quality and authenticity are expected to evolve significantly by 2026.
Article written by: Marcus Vane
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0






















































:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/iphone-17-pro-d7ae6571d5b147ab8312e83b4d30a5a9.jpg)