The Artemis Mission Update: NASA's Strategic Pivot to Mars Exploration
A deep-dive into the technical and geopolitical significance of the latest Artemis mission phases and the transition towards the first manned Mars landing.

The Artemis Mission Update: NASA's Strategic Pivot to Mars Exploration
Table of Contents
- Introduction to the Artemis Mission
- Current Progress and Achievements
- Challenges and Innovations
- The Strategic Shift Toward Mars
- International Collaborations and Treaties
- Conclusion
Introduction to the Artemis Mission
The Artemis mission, spearheaded by NASA, represents a groundbreaking initiative designed to return humans to the Moon and beyond, laying the groundwork for future manned missions to Mars. Since its inception, the program has aimed to demonstrate new technologies, capabilities, and business approaches required for the future of human space exploration. Named after the twin sister of Apollo, the program is not just about revisiting the Moon but establishing a sustainable human presence there by the end of the decade.
Current Progress and Achievements
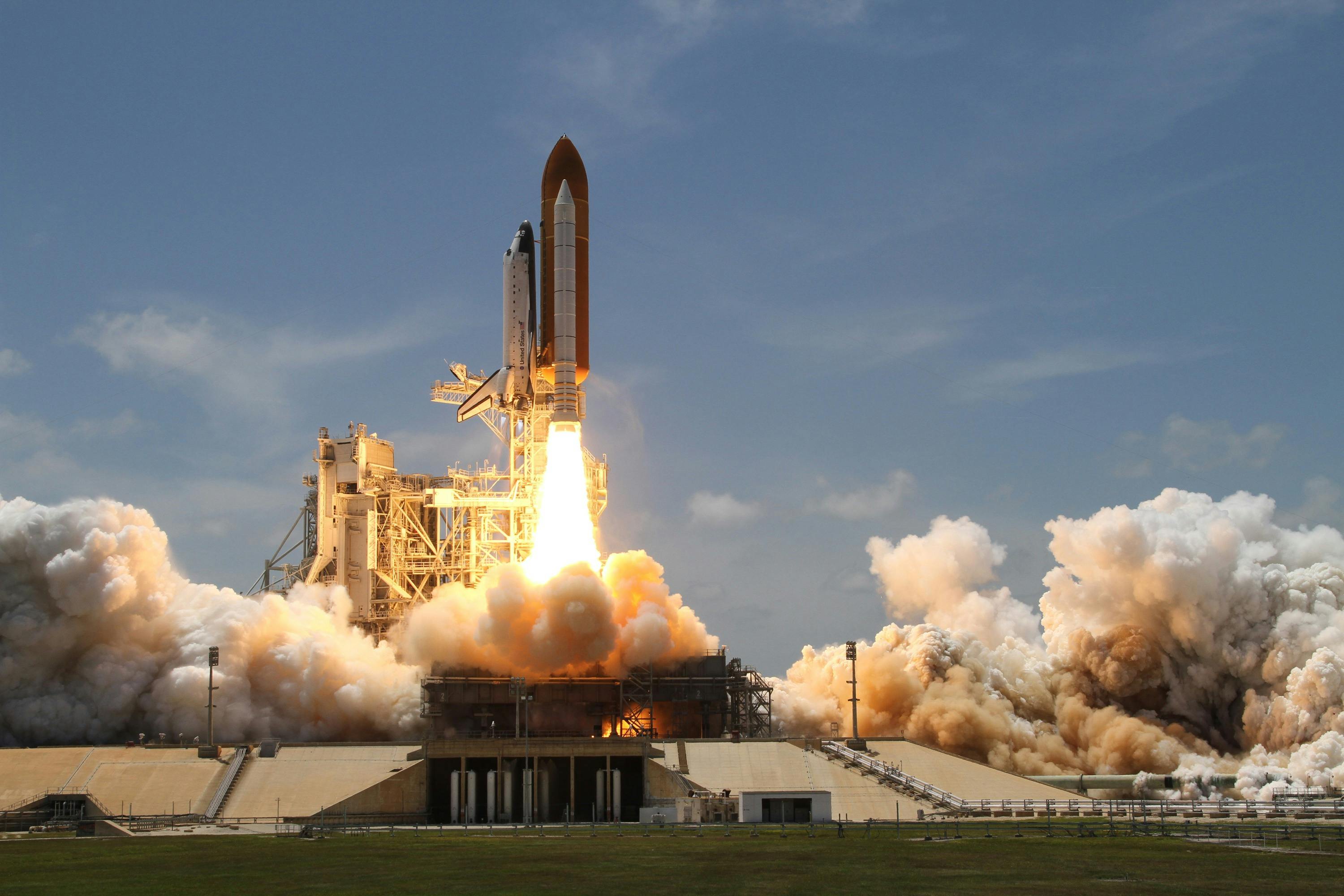
As of 2023, the Artemis program has made significant strides. NASA successfully launched the Artemis I mission in November 2022, marking the first integrated flight of the Space Launch System (SLS) and the Orion spacecraft. This uncrewed mission paved the way for subsequent human missions by testing critical systems and capabilities. The NASA Artemis I mission validated the spacecraft's performance in deep space and re-entry into Earth's atmosphere.
With Artemis II, planned for 2024, NASA intends to send astronauts on a flyby mission around the Moon, marking the first crewed mission since Apollo 17 in 1972. This endeavor will further test life-support systems and safety protocols in preparation for more extended lunar missions.
Challenges and Innovations
The Artemis program is not without its challenges. One of the primary obstacles is developing the Gateway, a lunar orbital platform that will support sustainable lunar operations by providing a staging point for missions to the Moon and eventually Mars. The technical complexity of constructing and maintaining a space station in lunar orbit requires innovative engineering solutions.
Additionally, NASA is working with commercial partners through its Next Space Technologies for Exploration Partnerships (NextSTEP) program, focusing on developing critical technologies such as the Human Landing System (HLS). These collaborations aim to lower costs and accelerate technological advancements, ensuring the program's success.
The Strategic Shift Toward Mars
NASA's long-term vision extends beyond the Moon, with Mars as the ultimate destination. The lessons learned and technologies developed during the Artemis missions will be instrumental in overcoming the challenges of a manned Mars mission. The agency's strategic pivot includes researching the effects of long-duration space travel on the human body and developing sustainable life-support systems.
Bill Nelson, the Administrator of NASA, highlighted the importance of international collaboration and commercial partnerships in achieving these goals. In a recent interview with Reuters, he emphasized the need for a global effort in advancing human space exploration.
International Collaborations and Treaties
The Artemis program is not an isolated endeavor; it involves significant international cooperation. NASA has established partnerships with the European Space Agency (ESA), the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), among others. These collaborations are crucial for sharing expertise, resources, and responsibilities in constructing and operating the Gateway.
Furthermore, the Artemis Accords, a set of principles for lunar and space exploration, have been signed by numerous countries. They emphasize transparency, interoperability, and the peaceful use of outer space. According to the New York Times, these accords align with the Outer Space Treaty of 1967, ensuring that space exploration remains a collaborative and peaceful endeavor.
Conclusion
The Artemis mission marks a pivotal moment in the history of space exploration, symbolizing humanity's return to the Moon and the ambition to reach Mars. Through technological innovation, international collaboration, and a strategic focus on sustainable exploration, NASA is paving the way for a new era of discovery. As we look to the future, the Artemis mission serves as a testament to human ingenuity and the boundless possibilities that lie ahead in our quest to explore the cosmos.
FAQ
What is the main goal of the Artemis mission?
The Artemis mission aims to return humans to the Moon and establish a sustainable presence there as a stepping stone for future manned missions to Mars.
When is the first crewed Artemis mission planned?
Artemis II, the first crewed mission of the Artemis program, is planned for 2024.
What role do international partnerships play in the Artemis program?
International partnerships are crucial for sharing expertise, resources, and responsibilities, as seen in collaborations with ESA, CSA, and JAXA, which are integral to the program's success.
How do the Artemis Accords relate to space exploration?
The Artemis Accords outline principles for transparent, peaceful, and collaborative space exploration, complementing the Outer Space Treaty of 1967.
Comprehensive Global Context and Expert Insights
Taking a broader perspective on this matter reveals that it is part of a larger, interconnected series of global events. The nuances involved require a balanced analysis that considers historical context alongside immediate impacts. Observers suggest that as more data becomes available, the long-term significance of this development will become clearer, potentially influencing policy and public perception across various regions. Our editorial team remains dedicated to monitoring these trends closely, ensuring that our readers receive the most accurate and in-depth information as the situation continues to unfold in the coming months.
Article written by: Elena Rodriguez
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0






















































:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/iphone-17-pro-d7ae6571d5b147ab8312e83b4d30a5a9.jpg)