US Housing Market 2026: Analyzing the National Supply and Affordability Crisis
A detailed analysis of why US housing prices remain at record highs and the legislative measures being proposed to tackle the national supply shortage.

US Housing Market 2026: Analyzing the National Supply and Affordability Crisis
Table of Contents
- Introduction to the Housing Crisis
- Factors Contributing to Supply Shortages
- Affordability: A Growing Concern
- Government and Industry Responses
- Future Outlook and Predictions
Introduction to the Housing Crisis
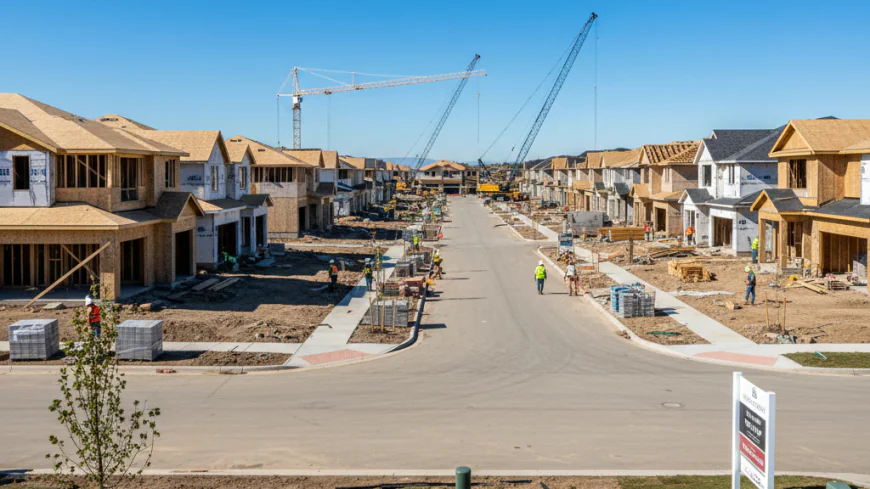
The United States is facing a significant housing crisis that is expected to intensify by 2026, with the National Association of Realtors warning of a historic supply shortage. The demand for housing, driven by population growth and changing demographics, continues to outpace the available supply. This imbalance results in skyrocketing prices, making homeownership and rental markets increasingly unaffordable for many Americans.
According to a New York Times report, the housing market is grappling with a deficit of approximately 5.5 million homes, affecting not only major metropolitan areas but also smaller towns and rural communities. This shortage exacerbates socio-economic disparities and presents challenges to policymakers and industry leaders alike.
Factors Contributing to Supply Shortages
Several factors contribute to the current housing supply shortage in the United States. Key among these is the shortage of skilled labor in the construction industry. As noted by the Associated Press, the industry struggles to replace an aging workforce, and fewer young people are entering the field.
Additionally, the rising cost of building materials, exacerbated by supply chain disruptions during the COVID-19 pandemic, has created financial hurdles for developers. Tariffs on imported materials and inflationary pressures further increase costs, making it economically unfeasible for many builders to commence new projects.
Land-use policies and zoning laws also play a critical role in constraining supply. In many urban centers, restrictive zoning laws limit the type and density of housing that can be built, resulting in underutilized spaces that could otherwise accommodate additional housing units. A Reuters analysis highlighted that reforming these policies could unlock potential housing sites, yet political and community resistance often stymies efforts to make such changes.
Affordability: A Growing Concern
The affordability of housing remains a pressing issue, with median home prices rising faster than incomes. Data from the U.S. Census Bureau indicates that housing costs have increased by 30% over the past five years, while median household income grew by only 15% in the same period.
This disparity is particularly acute in cities like San Francisco, Los Angeles, and New York, where the cost of living is exorbitant. However, even traditionally affordable regions are experiencing similar trends, as remote work and lifestyle preferences drive individuals to suburban and exurban areas, increasing competition and prices.
Rental affordability is also problematic. A U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development study found that nearly half of all renters spend more than 30% of their income on housing, a threshold commonly used to determine affordability. This situation leaves many households vulnerable to financial insecurity and displacement.
Government and Industry Responses
In response to the housing crisis, both government bodies and private sectors are taking various initiatives to address supply and affordability issues. The Biden administration has introduced several measures aimed at increasing housing supply, including incentives for local governments to reform zoning laws and investments in affordable housing projects.
The White House has also proposed increasing funding for the Housing Trust Fund, which focuses on the development of housing for extremely low-income families. Moreover, tax credits for builders and developers who create affordable housing units are being considered as a way to stimulate supply.
On the industry side, companies are increasingly adopting innovative construction techniques to reduce costs and accelerate building timelines. Prefabricated and modular homes, for instance, offer a more efficient and sustainable alternative to traditional construction methods. These approaches, combined with technological advancements in materials and design, show promise in bridging the supply gap.
Future Outlook and Predictions
Looking ahead to 2026, the outlook for the U.S. housing market remains uncertain, with experts offering varied predictions. Some analysts, such as those at the Zillow Economic Research, are optimistic that policy reforms and technological innovations will gradually alleviate supply constraints and improve affordability.
Others, however, caution that without substantial changes in land-use policies and a concerted effort to address labor shortages, the crisis could persist. The ongoing economic challenges, including potential recessions and interest rate fluctuations, could further complicate these efforts.
The role of environmental considerations also cannot be overlooked. As climate change impacts become more pronounced, the selection of sustainable building practices and the location of new developments will be crucial factors in the planning process.
Ultimately, the resolution of the housing crisis will require a collaborative approach, involving government entities, industry leaders, and community stakeholders. Only through coordinated action can the nation hope to achieve a balanced housing market that meets the needs of all its citizens.
FAQ
- What are the main causes of the housing supply shortage?
The primary causes include a shortage of skilled labor, high costs of building materials, and restrictive zoning laws that limit housing development.
- How is the government addressing the housing crisis?
The government is implementing measures such as zoning reform incentives, increased funding for affordable housing, and tax credits for developers.
- What role does technology play in solving the housing shortage?
Technology facilitates innovative construction methods like prefabricated and modular homes, which can reduce costs and construction time.
Strategic Financial Outlook and Market Dynamics
The current economic indicators suggest a period of recalibration for both individual investors and large-scale institutions. Analysts emphasize that navigating this volatility requires a multifaceted approach, blending traditional risk management with an awareness of emerging global trends. The correlation between consumer spending shifts and broader fiscal policies is becoming more pronounced, forcing businesses to adapt their long-term growth strategies. As central banks continue to monitor these fluctuations, transparency and proactive communication will remain key factors in maintaining market confidence and economic stability through the next fiscal year.
Article written by: Marcus Vane
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0






















































:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/iphone-17-pro-d7ae6571d5b147ab8312e83b4d30a5a9.jpg)