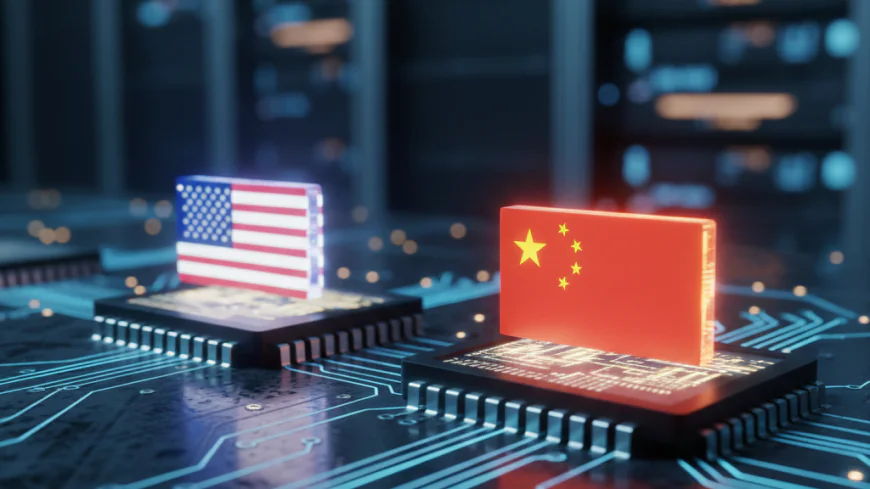
US-China Trade War 2.0: The Global Semiconductor Supremacy Race
Examining the intensifying trade restrictions on microchip technology between Washington and Beijing and its impact on the global supply chain.

US-China Trade War 2.0: The Global Semiconductor Supremacy Race
Table of Contents
- Introduction to the Semiconductor Supremacy Race
- The Stakes: Why Semiconductors Matter
- US Strategy: Protecting and Promoting Innovation
- China's Ambitions and Strategic Moves
- Global Implications and Future Prospects
Introduction to the Semiconductor Supremacy Race
The escalating tensions between the United States and China have taken a new turn with the focus shifting to semiconductors, a cornerstone of the modern digital economy. The two superpowers are vying for dominance in this critical industry, which is pivotal not only for technological advancements but also for national security. This new phase of the trade war is being termed as the "Semiconductor Supremacy Race."
President Joe Biden has been actively pursuing policies to bolster the US semiconductor industry. Meanwhile, Xi Jinping, President of China, has made it a national priority to reduce dependence on foreign technology and nurture domestic semiconductor capabilities.
The Stakes: Why Semiconductors Matter
Semiconductors, often referred to as the "brains" of modern electronics, are integral to the functioning of everything from smartphones to advanced military systems. According to the Semiconductor Industry Association, the global semiconductor market was valued at over $500 billion in 2021, emphasizing its economic significance.
The strategic importance of semiconductors is underscored by their role in emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), 5G communications, and Internet of Things (IoT). These technologies are expected to drive future economic growth and innovation, making semiconductor control a key aspect of national power.
US Strategy: Protecting and Promoting Innovation
To maintain its competitive edge, the United States has implemented several measures aimed at protecting its semiconductor industry. In 2021, the U.S. Department of Commerce and other government bodies announced significant investments and incentives to spur innovation and manufacturing capabilities domestically.
Additionally, the US has taken steps to limit Chinese access to cutting-edge semiconductor technologies. This includes export controls and blacklisting Chinese firms such as Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corporation (SMIC).
The American Jobs Plan proposed by President Biden includes $50 billion to strengthen the semiconductor industry, with a focus on research and development (R&D) and manufacturing.
China's Ambitions and Strategic Moves
China is equally committed to advancing its semiconductor capabilities. The country has launched initiatives under its "Made in China 2025" strategy to achieve self-sufficiency in semiconductor manufacturing. According to the Chinese Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, they are determined to significantly increase local production of semiconductors by 2025.
China has invested heavily in its domestic semiconductor industry, leveraging both state-owned enterprises and private firms. The government is also fostering partnerships with foreign companies to gain access to advanced technologies and expertise.
The rise of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. as a global telecommunications giant exemplifies China's ambitions in this realm. Despite facing US sanctions, Huawei continues to invest in semiconductor R&D, striving to overcome reliance on foreign technology.
Global Implications and Future Prospects
The semiconductor supremacy race between the US and China has profound implications for the global economy and geopolitical landscape. Other nations are also being drawn into this tech rivalry, with countries like South Korea and Taiwan playing pivotal roles due to their advanced semiconductor industries.
The global supply chain disruptions experienced during the COVID-19 pandemic have highlighted the vulnerabilities associated with semiconductor production, prompting countries worldwide to reassess their strategies. In response, the European Union and Japan are also ramping up efforts to boost domestic semiconductor production.
As the US and China continue to jockey for dominance, the future of the semiconductor industry will shape the next generation's economic and technological paradigms. The outcome of this competition will influence global power dynamics, impacting everything from trade policies to military strategies.
In conclusion, the US-China trade war has evolved into a battle over semiconductor supremacy. The stakes are high, with both nations investing heavily to secure their positions. Policymakers and industry leaders worldwide are closely monitoring this race, as its outcome will determine the future of technology and international relations.
FAQ
- What are semiconductors, and why are they important?
Semiconductors are materials that have a conductivity between conductors and insulators. They are essential components in electronic circuits, powering devices such as smartphones, computers, and advanced military systems. Their importance lies in their role in emerging technologies like AI and 5G, which are expected to drive future economic growth.
- How is the US government supporting its semiconductor industry?
The US government has implemented various measures, including significant investments in R&D and manufacturing, to bolster its semiconductor industry. The American Jobs Plan includes $50 billion to strengthen the sector, emphasizing innovation and domestic production capabilities.
- What steps is China taking to advance its semiconductor capabilities?
China has launched initiatives under its "Made in China 2025" strategy to achieve self-sufficiency in semiconductor manufacturing. The government is investing heavily in domestic production and fostering partnerships to gain access to advanced technologies.
- What are the global implications of the US-China semiconductor race?
The semiconductor race between the US and China has significant implications for the global economy and geopolitics. Other nations, such as South Korea and Taiwan, play key roles due to their advanced industries. The competition influences global power dynamics, impacting trade policies and military strategies.
- What are the challenges facing the global semiconductor supply chain?
The global supply chain has been disrupted by various factors, including the COVID-19 pandemic, highlighting vulnerabilities in semiconductor production. In response, countries are reassessing their strategies to enhance domestic production and reduce dependence on imports.
Comprehensive Global Context and Expert Insights
Taking a broader perspective on this matter reveals that it is part of a larger, interconnected series of global events. The nuances involved require a balanced analysis that considers historical context alongside immediate impacts. Observers suggest that as more data becomes available, the long-term significance of this development will become clearer, potentially influencing policy and public perception across various regions. Our editorial team remains dedicated to monitoring these trends closely, ensuring that our readers receive the most accurate and in-depth information as the situation continues to unfold in the coming months.
Article written by: Robert H. Miller
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0






















































:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/iphone-17-pro-d7ae6571d5b147ab8312e83b4d30a5a9.jpg)