Diminishing Waters: A Comprehensive Analysis of the Rio Grande Basin's Water Crisis
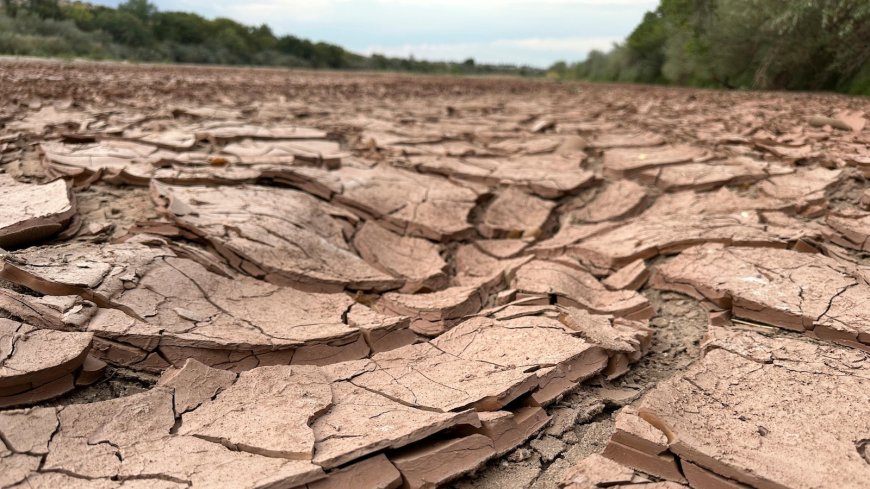

As the Rio Grande and its tributaries continue to dwindle, researchers have completed a meticulous assessment of water uses and losses in the Rio Grande-Bravo basin, shedding light on the escalating water security crisis that threatens communities and ecosystems in both the United States and Mexico. This vital waterway, which serves as a natural border between the two nations, is facing unprecedented challenges as climate change, population growth, and over-extraction converge to exacerbate water shortages.
The Rio Grande, known as the Río Bravo in Mexico, has historically been a lifeline for agriculture, industry, and urban populations. However, a recent study conducted by a coalition of hydrologists, climatologists, and environmental scientists reveals alarming trends that could have far-reaching implications for the region.
Comprehensive Global Context and Expert Insights
Taking a broader perspective on this matter reveals that it is part of a larger, interconnected series of global events. The nuances involved require a balanced analysis that considers historical context alongside immediate impacts. Observers suggest that as more data becomes available, the long-term significance of this development will become clearer, potentially influencing policy and public perception across various regions. Our editorial team remains dedicated to monitoring these trends closely, ensuring that our readers receive the most accurate and in-depth information as the situation continues to unfold in the coming months.
Article written by: Elena Rodriguez
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
1
Like
1
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0






















































:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/iphone-17-pro-d7ae6571d5b147ab8312e83b4d30a5a9.jpg)